In computer networking, communication between devices occurs in the form of packets. These packets are sent and received through different layers of the network protocol stack. To transmit a packet from one device to another, the sender must know the hardware address of the receiver. This is where the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) comes into play. In this article, we will take a deep dive into ARP and explain everything you need to know about it.
What is Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)?
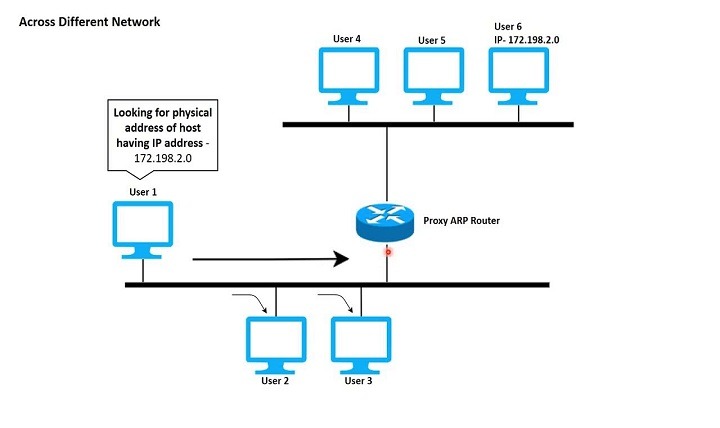
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol used in computer networks to map a network address (such as an IP address) to a physical address (such as a MAC address). It is used to resolve the layer 2 (data link layer) address of a device from a layer 3 (network layer) address. ARP is used by devices on the same network to communicate with each other.
How ARP Works:
When a device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends an ARP request broadcast message to all devices on the network. The message contains the IP address of the target device. The device with the matching IP address sends an ARP reply message to the sender, containing its MAC address. The sender then uses the MAC address to transmit the packet to the target device.
ARP Cache:
To improve performance, devices keep an ARP cache that stores the mapping of IP addresses to MAC addresses. This cache is used to avoid the need for ARP requests for frequently accessed devices. The cache is updated periodically to remove stale entries.
For more query about this type of similar topics, you can read this article: Upsssc Pet Admit Card
ARP Spoofing:
ARP spoofing is a technique used by attackers to intercept network traffic. The attacker sends fake ARP messages to the devices on the network, tricking them into sending traffic to the attacker instead of the intended device. To prevent ARP spoofing, network administrators can use techniques like port security and ARP spoofing detection tools.
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol used in computer networks to map a network address to a physical address. It is an essential part of communication between devices on the same network. ARP works by sending broadcast messages to all devices on the network to resolve the MAC address of a device from its IP address. ARP cache is used to improve performance, and ARP spoofing is a technique used by attackers to intercept network traffic. By understanding ARP and its workings, network administrators can ensure the security and efficiency of their networks.
Main points:
- ARP is a protocol used in computer networks to map a network address to a physical address.
- ARP is used to resolve the layer 2 (data link layer) address of a device from a layer 3 (network layer) address.
- ARP is used by devices on the same network to communicate with each other.
- When a device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it sends an ARP request broadcast message to all devices on the network.
- ARP cache is used to avoid the need for ARP requests for frequently accessed devices.
- ARP spoofing is a technique used by attackers to intercept network traffic.
- Network administrators can use techniques like port security and ARP spoofing detection tools to prevent ARP spoofing.